

Trusting Boundary Bay means you're never alone in facing your pet's health emergencies. Learn more about Animal Poisoning Treatment Surrey here This personalized approach ensures that your furry friend's specific needs are met, taking into account their medical history, the nature of their illness or injury, and their unique physical and emotional requirements. First, stay calm. Our team provides detailed care instructions, including medication management, wound care, and signs of complications to watch for.
Moreover, we've invested in the latest surgical equipment, ensuring that whether it's a routine procedure or a complex surgery, your pet's in the safest hands.
These stories and many more like them underscore the hospital's vital role in Animal Poisoning Treatment Surrey. Emergency infection treatment for pets Surrey We're equipped with state-of-the-art surgical suites that allow our skilled surgeons to perform a wide range of procedures, from urgent life-saving surgeries to complex orthopedic repairs. The hospital's in-house laboratory speeds up the process of getting test results, meaning treatment can start sooner rather than later. To address your pet's unique needs, the emergency vet hospital in Animal Poisoning Treatment Surrey offers a range of specialized treatment options. With gentle handling, soothing voices, and a patient approach, they minimize anxiety and fear, making the treatment process as smooth as possible.
Your pet is treated as a valued member of your family, deserving of the highest standard of care and compassion.
| Entity Name | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Emergency | Refers to critical care and immediate medical attention for animals in cases of accidents or sudden illness. | Source |
| Intensive care medicine | Specialized medical care for patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses and injuries that require close monitoring and support. | Source |
| Pet | A domesticated animal kept for companionship or pleasure, commonly requiring veterinary care for health and wellness. | Source |
| Veterinarian | A medical professional trained to diagnose, treat, and prevent illnesses in animals. | Source |
| Lower Mainland | A geographic region in British Columbia, Canada, encompassing the city of Surrey and surrounding areas, where emergency vet services are accessible. | Source |
| Major trauma | Refers to severe physical injuries that require immediate medical intervention, often provided in trauma centers. | Source |
| Trauma center | A specialized medical facility equipped to provide critical care and treatment for severe injuries. | Source |
| Emergency department | The part of a hospital or clinic focused on providing urgent care for acute medical issues. | Source |
| Walk-in | A service allowing patients to seek medical care without an appointment, useful in emergencies. | Source |
| Oxygen therapy | Medical treatment that provides extra oxygen for patients with breathing difficulties, commonly used in emergency care. | Source |
| Magnetic resonance imaging | An imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body, helpful in diagnosing medical conditions. | Source |
| CT scan | An imaging procedure that combines X-ray measurements to produce cross-sectional views of the body, used in diagnostics and trauma care. | Source |
| Endoscopy | A procedure using a flexible camera to view the internal organs, often for diagnostic purposes in emergency settings. | Source |
| X-ray image intensifier | A device that amplifies X-ray images, enabling clearer imaging for accurate diagnosis of injuries and conditions. | Source |
| Fluoroscopy | An imaging technique that shows real-time moving images, useful for guiding certain emergency procedures. | Source |
| Emergency Vets | Veterinarians specialized in providing urgent medical care to animals, often available 24/7 for critical cases. | Source |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) | An emergency procedure performed to manually restore circulation and breathing in patients who have experienced cardiac arrest. | Source |
| Cardiac arrest | A medical emergency where the heart stops beating, requiring immediate intervention like CPR to prevent death. | Source |
| Neurology | The branch of medicine dealing with the nervous system and related disorders, often involved in emergency treatment of neurological conditions. | Source |
| Internal medicine | The branch of medicine focused on diagnosing and treating internal organ systems, including in emergency veterinary care. | Source |
| Cardiology | The study and treatment of heart-related conditions, including emergency intervention for cardiac events. | Source |
| Oncology | The medical field focused on diagnosing and treating cancer, sometimes involving emergency care for critical cases. | Source |
| Radiology | The branch of medicine using imaging technology like X-rays and MRIs to diagnose and treat conditions, essential in emergency settings. | Source |
| Surrey | A city in British Columbia, Canada, where emergency vet services are available to support urgent animal care. | Source |
Surrey is a city in British Columbia, Canada. It is located south of the Fraser River on the Canada–United States border. It is a member municipality of the Metro Vancouver regional district and metropolitan area. Mainly a suburban city, Surrey is the province's second-largest by population after Vancouver and the third-largest by area after Abbotsford and Prince George. Seven neighbourhoods in Surrey are designated town centres: Cloverdale, Fleetwood, Guildford, Newton, South Surrey, and City Centre encompassed by Whalley.
Surrey was incorporated in 1879, and encompasses land formerly occupied by a number of Halqemeylem-speaking indigenous groups, including the Semiahmoo, Katzie, and the Kwantlen peoples. When Englishman H.J. Brewer looked across the Fraser River from New Westminster and saw a land reminiscent of his native County of Surrey in England, the settlement of Surrey was placed on the map. The area then comprised forests of douglas fir, fir, red cedar, hemlock, blackberry bushes, and cranberry bogs. A portion of present-day Whalley (named after Harry Whalley, who owned and operated a gas bar at the bend in King George Blvd, (formerly King George Highway) at 108 Avenue, "Whalley's Corner") was used as a burial ground by the Kwantlen (or Qw'ontl'en) Nation.
Settlers arrived first in Cloverdale and parts of South Surrey, mostly to farm, fish, harvest oysters, or set up small stores. Once the Pattullo Bridge was erected in 1937, the way was open for Surrey to expand. In the post-war 1950s, North Surrey's neighbourhoods filled with single-family homes and Surrey (not yet a city) became a bedroom community, absorbing commuters who worked in Burnaby or Vancouver.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the city witnessed unprecedented growth, as people from different parts of Canada and the world, particularly Asia, began to make the municipality their home. In 2013, it was projected to surpass the city of Vancouver as the most populous city in BC within the following 10 to 12 years.
Surrey is governed by the elected Surrey City Council comprising a mayor and eight councillors. As of the October 15, 2022, election, the mayor is Brenda Locke and city councillors are Linda Annis, Harry Bains,[a] Mike Bose, Doug Elford, Gordon Hepner, Pardeep Kooner, Mandeep Nagra, and Rob Stutt.
Remember, conditions like poisoning, seizures, and accidents require quick intervention to prevent further complications. Recognizing the signs that your pet urgently needs medical attention can save their life. The staff greets you warmly, ready to listen and address any concerns you might have.
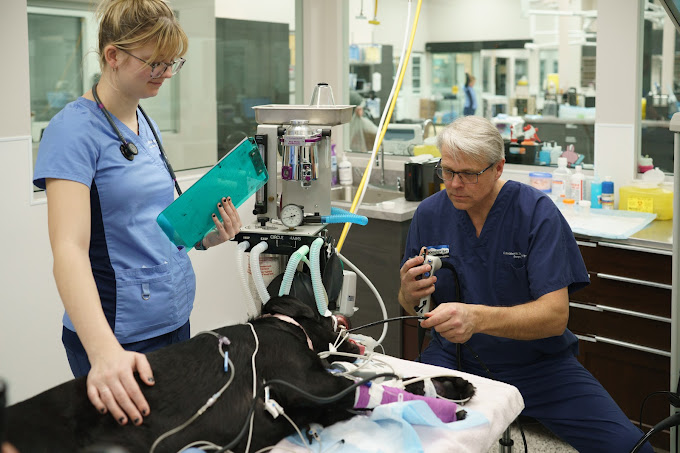
Our operating rooms are outfitted with advanced monitoring systems, guaranteeing that vital signs are closely watched throughout any procedure. Every staff member, from the front desk to the operating room, is dedicated to not just the physical well-being of your furry friend but also their emotional comfort. It's a commitment to not just heal but also educate the community, fostering a deeper understanding and connection between pets and their owners. Your job is to provide them with as much information as possible about your pet's health history and the current situation. When every second counts, the last thing you want is to be held back by the need for a referral.
Our emergency vet hospital offers an unparalleled range of services, ensuring your pet receives the best possible care in times of need. When your pet faces an emergency, your initial actions are crucial to their survival. We're set up to handle everything from trauma injuries to acute medical conditions, ensuring your pet gets the specific care they require. You'll find everything from high-resolution MRI and CT scans, which can uncover issues that standard X-rays might miss, to sophisticated ultrasound machines offering real-time views of your pet's internal organs.
Moreover, our hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities designed to handle a wide range of emergencies at any hour. With Boundary Bay's 24/7 availability, you can rest assured that your pet's health is in capable hands, day or night. Best emergency vet clinics in Surrey You'll find that we're equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, including high-definition MRI and CT scanners, which allow for precise imaging of your pet's condition in real-time. No matter what time of day or night, if you're faced with a pet emergency, don't hesitate to reach out.
Don't hesitate to reach out to a vet when every second counts. This is particularly reassuring during emergencies when time is of the essence. Don't worry if you haven't called ahead; the team is always ready to assist walk-ins. The specialists at Boundary Bay didn't just provide treatment; they offered compassion and support, explaining every step of the process.
Is your pet breathing? Together, we're making a difference, one paw at a time.
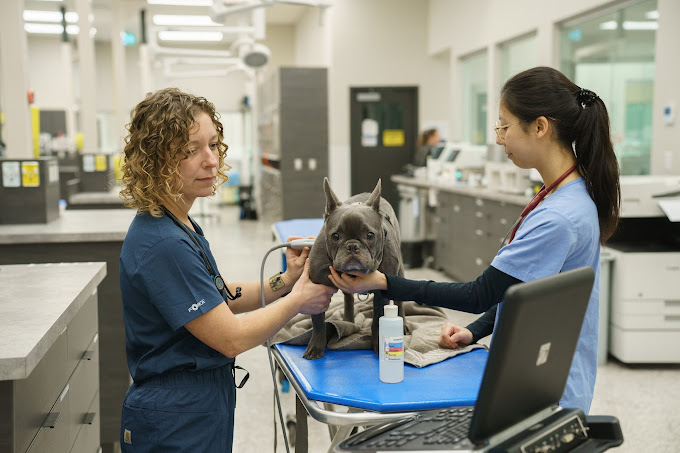


After exploring the state-of-the-art facilities, it's crucial to highlight the comprehensive resources available to pet owners for ongoing support and education. You'll find a collection of testimonials that speak volumes about the dedication and professionalism at this hospital. This might include medication schedules, dietary adjustments, or physical therapy exercises. You'll notice they take the time to explain complex medical terms in a way that's easy to understand, ensuring you're informed at every step of your pet's care journey. After recognizing the signs of a pet emergency, your next step is to contact Boundary Bay Veterinary Specialty Hospital for immediate assistance.
If they're used to a carrier, ensure it's secure and cozy with their favorite blanket or toy. Choosing Boundary Bay means prioritizing your pet's health with a team that values their well-being as much as you do. Let's take a moment to appreciate the skilled veterinarians and staff whose tireless efforts turn despair into hope. One dog owner mentioned, 'When my retriever injured his paw late at night, I was frantic.
Many pet emergencies, such as poisoning or severe injuries, can worsen without prompt treatment, leading to more complex and expensive medical issues. That means less stress for you and faster care for your furry friend. Understanding that each pet is unique, we tailor our care to meet their individual needs and preferences. In essence, our commitment to incorporating advanced medical technology means your pet benefits from the highest standard of care available around the clock.
When you walk into Boundary Bay, you're stepping into an environment equipped with the latest veterinary technology. Imagine it's late at night, and your beloved dog suddenly starts showing signs of severe distress. Critical newborn pet care Surrey It's our commitment to be there for you and your furry family member when you need us most. Our surgical suite is equipped for a variety of procedures, from spays and neuters to more complex operations, all performed with your pet's safety and comfort in mind.
Next, always have the contact information of Boundary Bay's emergency vet services in Animal Poisoning Treatment Surrey handy. Boundary Bay is committed to your pet's health, ensuring you have access to comprehensive emergency services without the need for a referral. Small animal emergency care Surrey They ensure you're fully informed about your pet's condition, treatment options, and care requirements. When you're faced with an urgent situation, the last thing you want to worry about is how you'll pay for your pet's care.
We understand the panic and fear that come with emergencies, so we've streamlined our services to ensure you and your pet receive the fastest, most efficient care possible. They're supported by veterinary nurses who provide round-the-clock care, ensuring your pet is comfortable and safe throughout their recovery. They're there to guide you through the process, from the moment you arrive to the time you leave, making sure you and your pet feel supported throughout your visit.
Imagine your furry friend in a crisis, feeling helpless and anxious. This immediate access to results can be a game-changer in the treatment of your beloved pet. You're not alone in these critical moments.
Our diagnostic capabilities include state-of-the-art imaging and lab tests, enabling accurate and swift diagnosis. Our team doesn't stop at veterinarians alone; it includes skilled veterinary nurses and technologists, all working seamlessly together to provide the highest level of care. So, when you're explaining your pet's symptoms or your concerns, they're actively listening and preparing to act swiftly.
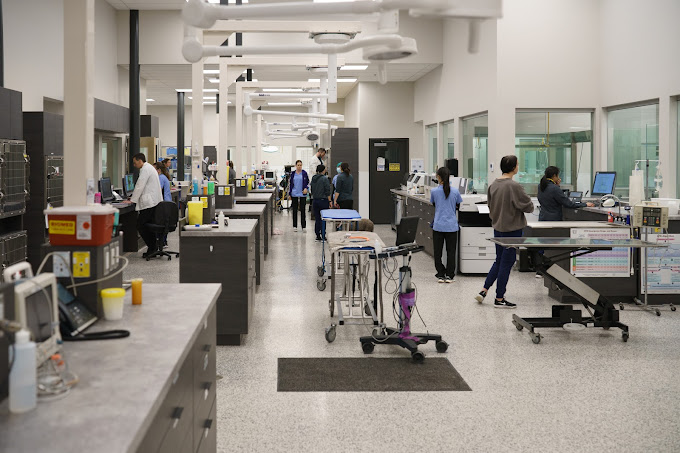



A veterinarian (vet) is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, veterinarians also play a role in animal reproduction, health management, conservation, husbandry and breeding and preventive medicine like nutrition, vaccination and parasitic control as well as biosecurity and zoonotic disease surveillance and prevention.

In many countries, the local nomenclature for a veterinarian is a regulated and protected term, meaning that members of the public without the prerequisite qualifications and/or license are not able to use the title. This title is selective in order to produce the most knowledgeable veterinarians that pass these qualifications. In many cases, the activities that may be undertaken by a veterinarian (such as treatment of illness or surgery in animals) are restricted only to those professionals who are registered as a veterinarian. For instance, in the United Kingdom, as in other jurisdictions, animal treatment may only be performed by registered veterinarians (with a few designated exceptions, such as paraveterinary workers), and it is illegal for any person who is not registered to call themselves a veterinarian, prescribe any drugs, or perform treatment.
Most veterinarians work in clinical settings, treating animals directly. These veterinarians may be involved in a general practice, treating animals of all types; they may be specialized in a specific group of animals such as companion animals, livestock, zoo animals or equines; or may specialize in a narrow medical discipline such as surgery, dermatology or internal medicine. As with other healthcare professionals, veterinarians face ethical decisions about the care of their patients.[1] Current debates within the profession include the ethics of certain procedures believed to be purely cosmetic or unnecessary for behavioral issues, such as declawing of cats, docking of tails, cropping of ears and debarking on dogs.[2]
The word "veterinary" comes from the Latin veterinae meaning "working animals". "Veterinarian" was first used in print by Thomas Browne in 1646.[3] Although "vet" is commonly used as an abbreviation in all English-speaking countries, the occupation is formally referred to as a veterinary surgeon in the United Kingdom and Ireland and now as a veterinarian in most of the rest of the English-speaking world.

Ancient Indian sage and veterinarian Shalihotra (mythological estimate c. 2350 BCE), the son of a sage, Hayagosha, is considered the founder of veterinary sciences.[4]

The first veterinary college was founded in Lyon, France, in 1762 by Claude Bourgelat.[5] According to Lupton, after observing the devastation being caused by cattle plague to the French herds, Bourgelat devoted his time to seeking out a remedy. This resulted in his founding a veterinary college in Lyon in 1761, from which establishment he dispatched students to combat the disease; in a short time, the plague was stayed and the health of stock restored, through the assistance rendered to agriculture by veterinary science and art.[6]

The Odiham Agricultural Society was founded in 1783 in England to promote agriculture and industry,[7] and played an important role in the foundation of the veterinary profession in Britain.[8] A 1785 Society meeting resolved to "promote the study of Farriery upon rational scientific principles."
The professionalization of the veterinary trade was finally achieved in 1790, through the campaigning of Granville Penn, who persuaded the Frenchman Charles Vial de Sainbel to accept the professorship of the newly established Veterinary College in London.[7] The Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons was established by royal charter in 1844.

Veterinary science came of age in the late 19th century, with notable contributions from Sir John McFadyean, credited by many as having been the founder of modern Veterinary research.[9]
Veterinarians treat disease, disorder or injury in animals, which includes diagnosis, treatment and aftercare. The scope of practice, specialty and experience of the individual veterinarian will dictate exactly what interventions they perform, but most will perform surgery (of differing complexity).
Unlike in human medicine, veterinarians must rely primarily on clinical signs, as animals are unable to vocalize symptoms as a human would. In some cases, owners may be able to provide a medical history and the veterinarian can combine this information along with observations, and the results of pertinent diagnostic tests such as radiography, CT scans, MRI, blood tests, urinalysis and others.
Veterinarians must consider the appropriateness of euthanasia ("putting to sleep") if a condition is likely to leave the animal in pain or with a poor quality of life, or if treatment of a condition is likely to cause more harm to the patient than good, or if the patient is unlikely to survive any treatment regimen. Additionally, there are scenarios where euthanasia is considered due to the constraints of the client's finances.
As with human medicine, much veterinary work is concerned with prophylactic treatment, in order to prevent problems occurring in the future. Common interventions include vaccination against common animal illnesses, such as distemper or rabies, and dental prophylaxis to prevent or inhibit dental disease. This may also involve owner education so as to avoid future medical or behavioral issues.
Additionally, veterinarians can play important roles in public health and the prevention of zoonoses.[10]

The majority of veterinarians are employed in private practice treating animals (75% of vets in the United States, according to the American Veterinary Medical Association).[11]
Small animal veterinarians typically work in veterinary clinics, veterinary hospitals, or both. Large animal veterinarians often spend more time travelling to see their patients at the primary facilities which house them, such as zoos or farms.
Other employers include charities treating animals, colleges of veterinary medicine, research laboratories, animal food companies, and pharmaceutical companies. In many countries, the government may also be a major employer of veterinarians, such as the United States Department of Agriculture or the Animal and Plant Health Agency in the United Kingdom. State and local governments also employ veterinarians.[12][13]
The COVID-19 pandemic has created a greater demand for veterinary services.[14] Many people are home with extra time on their hands, and adoption agencies and animals shelters have seen a surge in pet purchases as a result.[14] The American Veterinary Medical Association has provided COVID-19 resources for veterinarians on prevention measures, animal testing, and wellbeing.[15]
Veterinarians and their practices may be specialized in certain areas of veterinary medicine. Areas of focus include:
Veterinary specialists are in the minority compared to general practice veterinarians, and tend to be based at points of referral, such as veterinary schools or larger animal hospitals. Unlike human medicine, veterinary specialties often combine both the surgical and medical aspects of a biological system.
Veterinary specialties are accredited in North America by the AVMA through the American Board of Veterinary Specialties, in Europe by the European Board of Veterinary Specialisation and in Australia and New Zealand by the Australasian Veterinary Boards Council.[19][20][21] While some veterinarians may have areas of interest outside of recognized specialties, they are not legally specialists.
Specialties can cover general topics such as anesthesiology, dentistry, and surgery, as well as organ system focus such as cardiology or dermatology. A full list can be seen at veterinary specialties.
Many veterinarians, especially in large animal practice, offer house calls and farm calls through a mobile practice. The start-up and operating costs of a mobile practice are typically lower than those of a traditional brick and mortar hospital, which can cost millions of dollars or more for equipment and surgical supplies. Costs associated with mobile units can range from as low as $5,000 for a utility box in an SUV to around $250,000 for a fully equipped custom built chassis.[22] The potential advantages to the client are not having to transport the animal, lower stress for the animal, a lower risk of disease transmission from other animals, and convenience. A 2015 study published in the Journal of American Veterinary Medical Association proved that blood pressure readings, pulse rates and body temperature rates were increased by 11–16% when those readings were done in the clinic versus in the home.[23] However, mobile practices often lack the facilities and equipment to provide advanced care, surgery, or hospitalization. Some mobile practices maintain a relationship with a traditional hospital for referral of cases needing more comprehensive care.
The last AVMA Report on Veterinary Compensation, published in 2018, indicated private practice associate veterinarians who had board certification earned a mean of $187,000. A veterinarian's salary can easily exceed $300,000 depending on the specialty. The median starting salary for new veterinary graduates without specialization in 2018 was $103,800 in the United States according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, while the lowest paid earned less than $89,540 annually.[24] States and districts with the highest mean salary are California ($398,340), Michigan ($325,100), Illinois ($324,870), New York ($322,500), and Hawaii ($221,150).[25] Veterinarians who own their own clinics are typically paid a much higher salary. The average owner payout is $400,000 for every $1,000,000 of clinic income. In 2021 there were practices sold with $8–10,000,000 in yearly revenue with the owners drawing salaries of several million dollars. Over 90% of practice owners do not regret purchasing or starting their own practice, according to a 2020 survey of clinic owners.

In order to practice, vets must complete an appropriate degree in veterinary medicine, and in most cases must also be registered with the relevant governing body for their jurisdiction.
Degrees in veterinary medicine culminate in the award of a veterinary science degree, although the title varies by region. For instance, in North America, graduates will receive a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (Doctor of Veterinary Medicine or Veterinariae Medicinae Doctoris; DVM or VMD), whereas in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand or India they would be awarded a Bachelor of Veterinary Science, Surgery or Medicine (BVS, BVSc, BVetMed or BVMS), and in Ireland graduates receive a Medicinae Veterinariae Baccalaureus (MVB). In continental Europe, the degree of Doctor Medicinae Veterinariae (DMV, DrMedVet, Dr. med. vet., MVDr.) or Doctor Veterinariae Medicinae (DVM, DrVetMed, Dr. vet. med.) is granted.[26]
The award of a bachelor's degree was previously commonplace in the United States, but the degree name and academic standards were upgraded to match the 'doctor' title used by graduates.
Comparatively few universities have veterinary schools that offer degrees which are accredited to qualify the graduates as registered vets. For example, there are 30 in the United States, 5 in Canada, 1 in New Zealand, 7 in Australia (4 of which offer degrees accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA)), and 8 in the United Kingdom (4 of which offer degrees accredited by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA)).[27]
Due to this scarcity of places for veterinary degrees, admission to veterinary school is competitive and requires extensive preparation. In the United States in 2007, approximately 5,750 applicants competed for the 2,650 seats in the 28 accredited veterinary schools, with an acceptance rate of 46%.[28]
With competitive admission, many schools may place heavy emphasis and consideration on a candidate's veterinary and animal experience. Formal experience is a particular advantage to the applicant, often consisting of work with veterinarians or scientists in clinics, agribusiness, research, or some area of health science. Less formal experience is also helpful for the applicant to have, and this includes working with animals on a farm or ranch or at a stable or animal shelter and basic overall animal exposure.[29]
In the United States, approximately 80% of admitted students are female. In the early history of veterinary medicine of the United States, most veterinarians were males. However, in the 1990s this ratio reached parity, and now it has been reversed.
Preveterinary courses should emphasize the sciences. Most veterinary schools typically require applicants to have taken one year equivalent classes in organic, inorganic chemistry, physics, general biology; and one semester of vertebrate embryology and biochemistry. Usually, the minimal mathematics requirement is college level calculus. Individual schools might require introduction to animal science, livestock judging, animal nutrition, cell biology, and genetics. However, due to the limited availability of these courses, many schools have removed these requirements to widen the pool of possible applicants.
Following academic education, most countries require a vet to be registered with the relevant governing body, and to maintain this license to practice.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, veterinarians must be licensed to practice in the United States.[30] Licensing entails passing an accredited program, a national exam, and a state exam. For instance, in the United States, a prospective vet must receive a passing grade on a national board examination, the North America Veterinary Licensing Exam. This exam must be completed over the course of eight hours, and consists of 360 multiple-choice questions, covering all aspects of veterinary medicine, as well as visual material designed to test diagnostic skills.
The percentage electing to undertake further study following registration in the United States has increased from 36.8% to 39.9% in 2008. About 25% of those or about 9% of graduates were accepted into traditional academic internships. Approximately 9% of veterinarians eventually board certify in one of 40 distinct specialties from 22[31] specialty organizations recognized by the AVMA American Board of Veterinary Specialties (ABVS).[32][33]
Source:[34]
| Anesthesiology and analgesia | Animal welfare | Avian practice |
| Bacteriology and mycology | Beef cattle practice | Behavior |
| Canine and feline medicine | Cardiology | Dairy practice |
| Dentistry | Dermatology | Exotic animal medicine |
| Emergency and critical care | Equine medicine | Epidemiology |
| Laboratory animal medicine | Orthopaedics | Internal medicine |
| Pathology | Pharmacology | Poultry medicine |
| Reproductive medicine | Radiation oncology | Radiology |
| Shelter medicine | Surgery | Swine health management |
| Toxicology | Virology | Zoological medicine |
The first two-year curriculum in both veterinary and human medical schools are very similar in course names, but in certain subjects are relatively different in content. Considering the courses, the first two-year curriculum usually includes biochemistry, physiology, histology, anatomy, pharmacology, microbiology, epidemiology, pathology and hematology.[35]
Some veterinary schools use the same biochemistry, histology, and microbiology books as human medical students; however, the course content is greatly supplemented to include the varied animal diseases and species differences. In the past, many veterinarians were trained in pharmacology using the same text books used by physicians. As the specialty of veterinary pharmacology has developed, more schools are using pharmacology textbooks written specifically for veterinarians. Veterinary physiology, anatomy, and histology is complex, as physiology often varies among species. Microbiology and virology of animals share the same foundation as human microbiology, but with grossly different disease manifestation and presentations. Epidemiology is focused on herd health and prevention of herd borne diseases and foreign animal diseases. Pathology, like microbiology and histology, is very diverse and encompasses many species and organ systems. Most veterinary schools have courses in small animal and large animal nutrition, often taken as electives in the clinical years or as part of the core curriculum in the first two years.
The final two-year curriculum is similar to that of human medicine only in clinical emphasis.[35] A veterinary student must be well prepared to be a fully functional veterinarian on the day of graduation, competent in both surgery and medicine. The graduating veterinarian must be able to pass medical board examination and be prepared to enter clinical practice on the day of graduation, while most human medical doctors in the United States complete 3 to 5 years of post-doctoral residency before practicing medicine independently, usually in a very narrow and focused specialty. Many veterinarians do also complete a post-doctoral residency, but it is not nearly as common as it is in human medicine.
In the last years, curricula in both human and veterinary medicine have been adapted with the aim of incorporating competency-based teaching.[36][37] Furthermore, the importance of institutionalized systematic teacher feedback has been recognized and tools such as clinical encounter cards are being implemented in clinical veterinary education.[38]
Some veterinarians pursue post-graduate training and enter research careers and have contributed to advances in many human and veterinary medical fields, including pharmacology and epidemiology. Research veterinarians were the first to isolate oncoviruses, Salmonella species, Brucella species, and various other pathogenic agents. Veterinarians were in the forefront in the effort to suppress malaria and yellow fever in the United States. Veterinarians identified the botulism disease-causing agent, developed propofol; a widely used anesthetic induction drug,[39] produced an anticoagulant used to treat human heart disease,[40] and developed surgical techniques for humans, such as hip-joint replacement, limb and organ transplants.
Veterinarians work with a wide variety of animal species typically in hospitals, clinics, labs, farms, and zoos.[41] Veterinarians face many occupational hazards including zoonotic diseases, bites and scratches, hazardous drugs, needlestick injuries, ionizing radiation, and noise.[42][43][44] According to the U.S. Department of Labor, 12% of workers in the veterinary services profession reported a work-related injury or illness in 2016.[45]
Veterinary practices need a health and safety plan that addresses infection prevention and other hazards.[44][46] Workplaces should utilize engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment to keep their employees safe.[46][44] PPE such as gloves, safety goggles, lab coats, and hearing protection should be readily available with mandatory training on proper usage. Raising awareness is the most important step in promoting workplace health and safety.[45]
Needlestick injuries are the most common accidents among veterinarians, but they are likely underreported.[45][46][47] Needlesticks can result in hazardous drug or bloodborne-pathogen exposures.
Unlike human medical professionals, veterinarians receive minimal training on safe handling of hazardous drugs in school.[48] Also, a large percentage of veterinarians are women of reproductive age and drug exposures put them at risk of infertility or other adverse health outcomes.[48][49] Additionally, some antibiotics, steroids, and chemotherapy drugs are known to have negative effects on male fertility.[50] The U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has issued guidance on the safe handling of hazardous drugs for veterinary workers.[51] Animal bites and scratches are another common injury in veterinary practice.[43]
The close interactions with animals put veterinarians at increased risk of contracting zoonoses. A systematic review of veterinary students found that between 17% and 64% had acquired a zoonotic disease during their studies.[42] The animal species, work setting, health and safety practices, and training can all affect the risk of injury and illness.[42]
Noise can be a prominent exposure, in which case a hearing loss prevention program may be recommended. A NIOSH study on kennel noise found that noise levels often exceeded OSHA's permissible exposure limit.[52] Reducing noise is beneficial for animal and human health.[53][54]
Veterinarians have high suicide rates in comparison to the general population.[55] A study by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that male veterinarians are 2.1 times and female veterinarians are 3.5 times as likely as the general population to die by suicide.[55] Some reasons for this could be long hours, work overload, client expectations and complaints, poor remuneration, euthanasia procedures, and poor work-life balance.[55] A survey of more than 11,000 vets found 9% had serious psychological distress, 31% experienced depressive episodes, and 17% had suicidal ideation.[56] Online support groups, such as Not One More Vet, have been established to help veterinarians who may be experiencing suicidal thoughts.[57] NOMV educates veterinarians and vet techs about other ways to help themselves with mental health.[58] Another driver of stress can be student loan debt. A 2013 national survey found that average debt for veterinary medicine graduates was as high as $162,113.[59] Veterinarian lifelong earning potential is less than a physician, so it can take a lot longer to break even.[59]
Reality televisions shows featuring veterinarians include:
Fictional works featuring a veterinarian as the main protagonist include:
Most states in the US allow for malpractice lawsuit in case of death or injury to an animal from professional negligence. Usually the penalty is not greater than the value of the animal. Some states allow for punitive penalty, loss of companionship, and suffering, likely increasing the cost of veterinary malpractice insurance and the cost of veterinary care. Most veterinarians carry business, worker's compensation, and facility insurance to protect their clients and workers from injury inflicted by animals.[citation needed]
You'll find that some facilities offer accommodations for pet owners wanting to stay close to their pets during extended treatments or overnight emergencies, allowing you to be near your pet when they need you most.
You'll need to check directly with the hospital to see if they offer specialized care for exotic pets or wildlife emergencies, as services can vary and may require specific expertise or facilities.
Yes, you can participate in community outreach and educational programs offered by veterinary hospitals. These programs often include workshops, seminars, and preventive care education, helping you better care for your pet's health and wellbeing.